Docker Php Composer
- Installation & Setup
- Executing Commands
- Interacting With Databases
- Running Tests
- Docker Php Composer Tutorial
- Docker Php Composer Download
- Docker Php Composer Install
- Docker Php Composer Command
Introduction
Laravel Sail is a light-weight command-line interface for interacting with Laravel's default Docker development environment. Sail provides a great starting point for building a Laravel application using PHP, MySQL, and Redis without requiring prior Docker experience.
At its heart, Sail is the docker-compose.yml file and the sail script that is stored at the root of your project. The sail script provides a CLI with convenient methods for interacting with the Docker containers defined by the docker-compose.yml file.
Docker Desktop offers support for users subscribed to a Pro or a Team plan. If you are experiencing any issues with Docker Desktop, follow the instructions in this section to send a support request to Docker Support. Before you get started, we recommend that you sign into your Docker Desktop application and your Docker Hub account. Sail provides a great starting point for building a Laravel application using PHP, MySQL, and Redis without requiring prior Docker experience. At its heart, Sail is the docker-compose.yml file and the sail script that is stored at the root of your project. FROM php:7.2-fpm # Copy composer.lock and composer.json COPY composer.lock composer.json /var/www/ # Set working directory WORKDIR /var/www # Install dependencies RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y build-essential libpng-dev libjpeg62-turbo-dev libfreetype6-dev locales zip jpegoptim optipng pngquant gifsicle vim unzip.
Laravel Sail is supported on macOS, Linux, and Windows (via WSL2).
Installation & Setup
Laravel Sail is automatically installed with all new Laravel applications so you may start using it immediately. To learn how to create a new Laravel application, please consult Laravel's installation documentation for your operating system. During installation, you will be asked to choose which Sail supported services your application will be interacting with.
Installing Sail Into Existing Applications
If you are interested in using Sail with an existing Laravel application, you may simply install Sail using the Composer package manager. Of course, these steps assume that your existing local development environment allows you to install Composer dependencies:
After Sail has been installed, you may run the sail:install Artisan command. This command will publish Sail's docker-compose.yml file to the root of your application:
Finally, you may start Sail. To continue learning how to use Sail, please continue reading the remainder of this documentation:
Configuring A Bash Alias
By default, Sail commands are invoked using the vendor/bin/sail script that is included with all new Laravel applications:
However, instead of repeatedly typing vendor/bin/sail to execute Sail commands, you may wish to configure a Bash alias that allows you to execute Sail's commands more easily:
Once the Bash alias has been configured, you may execute Sail commands by simply typing sail. The remainder of this documentation's examples will assume that you have configured this alias:
Starting & Stopping Sail
Laravel Sail's docker-compose.yml file defines a Docker variety of containers that work together to help you build Laravel applications. Each of these containers is an entry within the services configuration of your docker-compose.yml file. The laravel.test container is the primary application container that will be serving your application.
Before starting Sail, you should ensure that no other web servers or databases are running on your local computer. To start all of the Docker containers defined in your application's docker-compose.yml file, you should execute the up command:
To start all of the Docker containers in the background, you may start Sail in 'detached' mode:
Once the application's containers have been started, you may access the project in your web browser at: http://localhost.
To stop all of the containers, you may simply press Control + C to stop the container's execution. Or, if the containers are running in the background, you may use the down command:
Executing Commands
When using Laravel Sail, your application is executing within a Docker container and is isolated from your local computer. However, Sail provides a convenient way to run various commands against your application such as arbitrary PHP commands, Artisan commands, Composer commands, and Node / NPM commands.
When reading the Laravel documentation, you will often see references to Composer, Artisan, and Node / NPM commands that do not reference Sail. Those examples assume that these tools are installed on your local computer. If you are using Sail for your local Laravel development environment, you should execute those commands using Sail:
Executing PHP Commands

PHP commands may be executed using the php command. Of course, these commands will execute using the PHP version that is configured for your application. To learn more about the PHP versions available to Laravel Sail, consult the PHP version documentation:
Executing Composer Commands
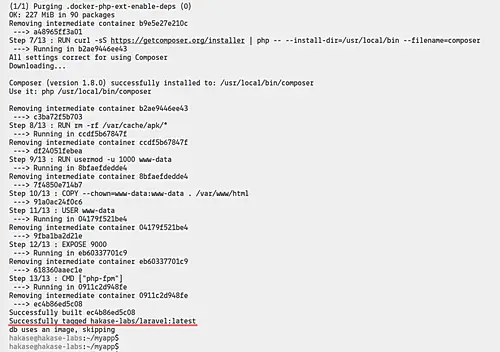
Composer commands may be executed using the composer command. Laravel Sail's application container includes a Composer 2.x installation:
Installing Composer Dependencies For Existing Applications
If you are developing an application with a team, you may not be the one that initially creates the Laravel application. Therefore, none of the application's Composer dependencies, including Sail, will be installed after you clone the application's repository to your local computer.
You may install the application's dependencies by navigating to the application's directory and executing the following command. This command uses a small Docker container containing PHP and Composer to install the application's dependencies:
Executing Artisan Commands
Laravel Artisan commands may be executed using the artisan command:
Executing Node / NPM Commands
Node commands may be executed using the node command while NPM commands may be executed using the npm command:
Interacting With Databases
MySQL
As you may have noticed, your application's docker-compose.yml file contains an entry for a MySQL container. This container uses a Docker volume so that the data stored in your database is persisted even when stopping and restarting your containers. In addition, when the MySQL container is starting, it will ensure a database exists whose name matches the value of your DB_DATABASE environment variable.

Once you have started your containers, you may connect to the MySQL instance within your application by setting your DB_HOST environment variable within your application's .env file to mysql.
To connect to your application's MySQL database from your local machine, you may use a graphical database management application such as TablePlus. By default, the MySQL database is accessible at localhost port 3306.
Redis
Your application's docker-compose.yml file also contains an entry for a Redis container. This container uses a Docker volume so that the data stored in your Redis data is persisted even when stopping and restarting your containers. Once you have started your containers, you may connect to the Redis instance within your application by setting your REDIS_HOST environment variable within your application's .env file to redis.
To connect to your application's Redis database from your local machine, you may use a graphical database management application such as TablePlus. By default, the Redis database is accessible at localhost port 6379.
MeiliSearch
If you chose to install the MeiliSearch service when installing Sail, your application's docker-compose.yml file will contain an entry for this powerful search-engine that is compatible with Laravel Scout. Once you have started your containers, you may connect to the MeiliSearch instance within your application by setting your MEILISEARCH_HOST environment variable to http://meilisearch:7700.
From your local machine, you may access MeiliSearch's web based administration panel by navigating to http://localhost:7700 in your web browser.
Running Tests
Laravel provides amazing testing support out of the box, and you may use Sail's test command to run your applications feature and unit tests. Any CLI options that are accepted by PHPUnit may also be passed to the test command:
The Sail test command is equivalent to running the test Artisan command:
Laravel Dusk
Laravel Dusk provides an expressive, easy-to-use browser automation and testing API. Thanks to Sail, you may run these tests without ever installing Selenium or other tools on your local computer. To get started, uncomment the Selenium service in your application's docker-compose.yml file:
Next, ensure that the laravel.test service in your application's docker-compose.yml file has a depends_on entry for selenium:
Finally, you may run your Dusk test suite by starting Sail and running the dusk command:
Previewing Emails
Laravel Sail's default docker-compose.yml file contains a service entry for MailHog. MailHog intercepts emails sent by your application during local development and provides a convenient web interface so that you can preview your email messages in your browser. When using Sail, MailHog's default host is mailhog and is available via port 1025:
Docker Php Composer Tutorial
When Sail is running, you may access the MailHog web interface at: http://localhost:8025
Container CLI
Sometimes you may wish to start a Bash session within your application's container. You may use the shell command to connect to your application's container, allowing you to inspect its files and installed services as well execute arbitrary shell commands within the container:
To start a new Laravel Tinker session, you may execute the tinker command:
PHP Versions
Sail currently supports serving your application via PHP 8.0 or PHP 7.4. To change the PHP version that is used to serve your application, you should update the build definition of the laravel.test container in your application's docker-compose.yml file:
In addition, you may wish to update your image name to reflect the version of PHP being used by your application. This option is also defined in your application's docker-compose.yml file:
Docker Php Composer Download
After updating your application's docker-compose.yml file, you should rebuild your container images:
Sharing Your Site
Sometimes you may need to share your site publicly in order to preview your site for a colleague or to test webhook integrations with your application. To share your site, you may use the share command. After executing this command, you will be issued a random laravel-sail.site URL that you may use to access your application:
If you would like to choose the subdomain for your shared site, you may provide the subdomain option when executing the share command:
{tip} The share command is powered by Expose, an open source tunneling service by BeyondCode.
Customization
Docker Php Composer Install
Since Sail is just Docker, you are free to customize nearly everything about it. To publish Sail's own Dockerfiles, you may execute the sail:publish command:
Docker Php Composer Command
After running this command, the Dockerfiles and other configuration files used by Laravel Sail will be placed within a docker directory in your application's root directory. After customizing your Sail installation, you may rebuild your application's containers using the build command:
